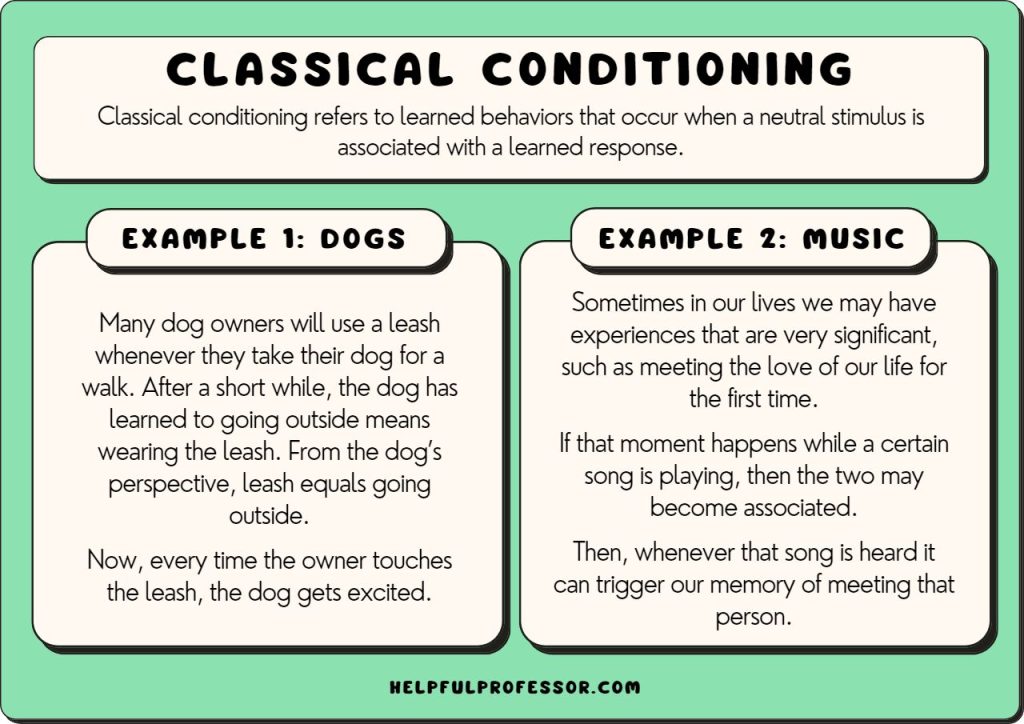
Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals . Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a.
from animalia-life.club
Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Ask the chatbot a question. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food.
Can You Train Your Dog Using Classical Conditioning
Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Ask the chatbot a question.
From thecutestlittleanimals.wordpress.com
Classical Conditioning the cutest little animals Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Pavlov was not the first scientist to. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From poshmark.com
Brighton Accessories Brighton Contempoglasses Logo Classic Handbag Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.pinterest.com
operant conditioning Operant conditioning, Dog training tips, Dog Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Pavlov. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.walmart.com
Zahari Home 13pc Contempo Bathroom Shower Curtain Sets Luxury Classic Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From courses.lumenlearning.com
Classical Conditioning Introduction to Psychology Reinke Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Web classical conditioning. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.pinterest.com
Classical Conditioning definition The learning process where an Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Pavlov showed. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.verywellmind.com
Classical Conditioning vs. Operant Conditioning Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Ask the chatbot a question. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From alisenberde.blogspot.com
CLASSICAL CONDITIONING EXAMPLES alisen berde Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Ask. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From resourcesatila.weebly.com
Ivan pavlov classical conditioning resourcesatila Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Ask the chatbot a question. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.dog-training-excellence.com
Classical Conditioning a basic form of learning. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From guatemaladigital.com
Aurora® Timeless Peanuts® Palm Pals™ Snoopy Stuffed Animal Classic Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From instituteofclinicalhypnosis.com
Classical Conditioning or (SOR) Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Ask the chatbot a question. Web classical conditioning. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.psychmechanics.com
A simple explanation of classical and operant conditioning Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From onet-connect-animal-classic-kkl.softonic.com
Connect Animal Classic para Android Descargar Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Ask the chatbot a question. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Classical. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Classical Conditioning PowerPoint Presentation, free download Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Pavlov's dog experiments played a critical role in the discovery of one of the most important concepts in psychology: Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Web for example, dogs don’t learn to salivate whenever they see food. Classical conditioning (also known as pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is learning through association and. Pavlov was. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Animal Behavior PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID9432018 Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Web for example,. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From www.verywellmind.com
Operant Conditioning How Does It Work? Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Ask the chatbot a question. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. In these experiments, the neutral signal was the. Classical conditioning (also. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.
From biologydictionary.net
Classical Conditioning The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals Pavlov showed that dogs could be conditioned to. Web classical conditioning refers to learning that occurs when a neutral stimulus (e.g., a tone) becomes associated with a stimulus (e.g., food) that naturally produces a. Pavlov was not the first scientist to study learning in animals, but he was the first to do. Ask the chatbot a question. Web for example,. Examples Of Classical Conditioning Animals.